고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
멋쟁이사자처럼 X K-DIGITAL Training - 07.15
[참고] 2021.07.14 - [python/k-digital] - [K-DIGITAL] 딥러닝 모델 최적화 이론
[K-DIGITAL] 딥러닝 모델 최적화 이론
멋쟁이사자처럼 X K-DIGITAL Training - 07.14 [이전] 2021.07.14 - [python/k-digital] - [K-DIGITAL] 머신러닝을 넘어 딥러닝으로 [K-DIGITAL] 머신러닝을 넘어 딥러닝으로 멋쟁이사자처럼 X K-DIGITAL Training..
juran-devblog.tistory.com
ijo0r98/likelion-kdigital
[국비교육] AI 인재 양성 프로그램. Contribute to ijo0r98/likelion-kdigital development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
Tensorflow
인공지능 애플리케이션 구축을 위하여 유연하고 다양한 기능을 제공하는 오픈소스 딥러닝 프레임워크
구글 브레인 팀에서 2015년 오픈소스로 공개했으며 실제 코드가 실행되는 환경은 C/C++
* Tensor
TensorFlow의 기본 자료 구조(타입)으로 다차원 배열(벡터의 확장)
* Graph
연산에 대해 정의한 것
tensor와 node간의 계산 등 포함한 설계도 의미
session을 통해(session에서) 실행
[텐서플로우 수행 단계]
1) Building a TensorFlow Graph
tensor들 사이 연산관계를 계산 그래프로 정의, 선언
2) Executing the TensorFlow Graph
계산 그래프에 정의된 연산을 tf.Session을 통해 실제로 실행
TensorFlow
모두를 위한 엔드 투 엔드 오픈소스 머신러닝 플랫폼입니다. 도구, 라이브러리, 커뮤니티 리소스로 구성된 TensorFlow의 유연한 환경입니다.
www.tensorflow.org
라이브러리
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR) # tf log
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# warning
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'tf.logging.set_verbosity 텐서플로우 로깅 타입 - error, debug, info, warn, fatal
1. 데이터 준비
MNIST (Mized National Institute of Standards and Technology database)
숫자 0~9 손글씨 이미지 데이터
각 이미지는 가로, 세로 28px의 흑백 이미지로 만들어져 있음
training data 55000장, validation data 5000장, test data는 10000장으로 구성되어 있음

from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./mnist/data/", one_hot=True)자동으로 다운받아 해당 경로에 데이터 생성
이미지에 대한 정보
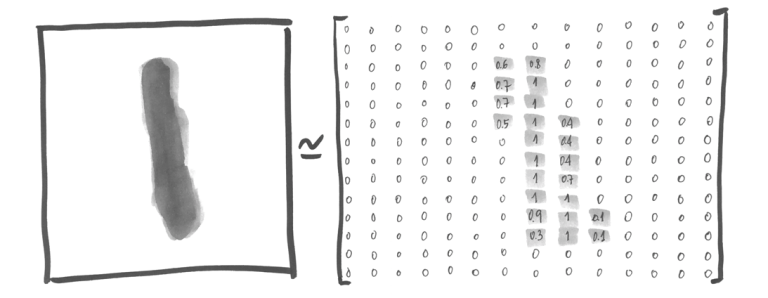
mnist.train.images.shape>> (55000, 784)
이미지에 대한 답은 one-hot vector 형태로 주어짐
pd.DataFrame(mnist.train.label) # 데이터프레임으로 확인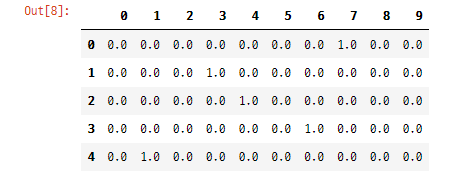
2. 모델 생성
# input
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 총 열의 개수 (28px*28px)
# output
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # 정답 열의 수 0~9행의 수는 지정하지 않고(None) 열의 수만 지정
* placeholder
tf.placeholder(
dtype,
shape=None,
name=None
)그래프에 사용할 입력값을 나중에 받기 위해 비워두는 매개변수, 데이터가 담겨있지 않은 빈 객체
2 hidden layers
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.01)) # 256: X 열의 수, 랜덤 정규분포 표준편차 0.01
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1)) # 활성화함수 타입 ReULW2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256, 256], stddev=0.01)) # 256: W1 열의 수
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2))W3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256, 10], stddev=0.01)) # 10: W2 열의 수
model = tf.matmul(L2, W3)
3. Criterion 설정
cost = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(Y, model)
# 마지막 퍼셉트론의 열은 output 개수만큼 있어야함
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)비용함수로 softmax 적용하여 cross entropy 구함 (분류 분석에 대한 오차)
cost function의 gradient descent 최적화 방법으로 AdamOptimizer(learning rate=0.001) 사용
4. 모델 학습
# session 초기화
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)mini batch
batch_size = 100 # 100행 per batch * 550 batches
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)# 550 * 15 = 8250 -> 총 8250 iteration (gd 실행 횟수)
for epoch in range(15):
total_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch): # 55000장 이미지를 대상으로 100장씩 550회 나눠서
# 55000장 중 랜덤으로 100장 꺼내는 코드 (비복원 추출) - mnist에서만 사용
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
_, cost_val = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys})
total_cost += cost_val
test_cost = sess.run([cost], feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels}) # current test error
print('Epoch: {}'.format(epoch+1),
'|| Avg. Training cost = {:.3f}'.format(total_cost / total_batch),
'|| Current Test cost = {:.3f}'.format(test_cost[0]))
print('Learning process is completed!')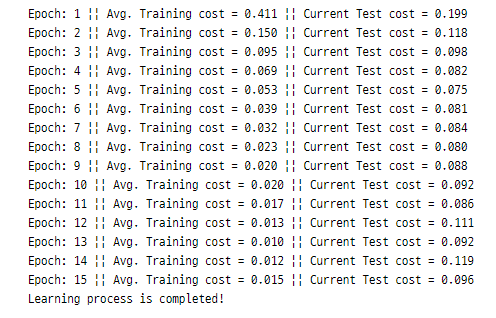
++) shuffle_batch 함수 적용
# batch suffle
def shuffle_batch(X, y, batch_size):
rnd_idx = np.random.permutation(len(X))
n_batches = len(X) // batch_size
for batch_idx in np.array_split(rnd_idx, n_batches):
X_batch, y_batch = X[batch_idx], y[batch_idx]
yield X_batch, y_batch
for epoch in range(15):
total_cost = 0
# mini batch
for batch_xs, batch_ys in shuffle_batch(X_train, y_train, batch_size):
_, cost_val = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys})
total_cost += cost_val
test_cost = sess.run([cost], feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels})
print('Epoch: {}'.format(epoch+1),
'|| Avg. Training cost = {:.3f}'.format(total_cost / total_batch),
'|| Current Test cost = {:.3f}'.format(test_cost[0]))
print('Learning process is completed!')
5. 성능 확인
is_correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(model, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1)) # model: 예측값, Y: 실제 정답
# 같으면 true, 다르면 false
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct, tf.float32))
print('정확도 :', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels}))>> 정확도 : 0.9786
+) Dropout 추가
일부 뉴런을 랜덤으로 삭제(drop)하여 과적합 방지
* 전체 인공신경망이 깊을 때(layer가 많을 때) 마지막 혹은 마지막 2개의 layer에 적용
# placeholder 동일
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 총 열의 개수 (28px*28px)
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) # 정답 열의 수 0~9
# dropout 비율
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# layer
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.01))
L1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(X, W1))
L1 = tf.nn.dropout(L1, keep_prob) # Dropout을 적용할 layer, 유지시킬 비율
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256, 256], stddev=0.01))
L2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(L1, W2))
L2 = tf.nn.dropout(L2, keep_prob) # Dropout을 적용할 layer, 유지시킬 비율
W3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256, 10], stddev=0.01))
model = tf.matmul(L2, W3)# set the criterion
cost = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(Y, model)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
# init
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# mini batch
batch_size = 100
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
print(total_batch)
# train
for epoch in range(15):
total_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, cost_val = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs,
Y: batch_ys,
keep_prob: 0.8})
# keep_prob: 살릴 비율 지정, node 중 80%만 유지하고 20%를 train 시마다 off
total_cost += cost_val
print('Epoch: {}'.format(epoch+1),
'Avg. cost =', '{:.3f}'.format(total_cost / total_batch))
print('Learning process is completed!')# test에서는 dropout 적용하지 않음 (keep_prob=1)
is_correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(model, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct, tf.float32))
print('정확도:', sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1}))>> 정확도: 0.9807
'PYTHON > K-DIGITAL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [K-DIGITAL] sklearn / tf 모델 저장 & Keras Callbacks API (0) | 2021.07.16 |
|---|---|
| [K-DIGITAL] 딥러닝 Tensorflow2.x 실습 - MNIST (0) | 2021.07.16 |
| [K-DIGITAL] 딥러닝 모델 최적화 이론 (0) | 2021.07.14 |
| [K-DIGITAL] 머신러닝을 넘어 딥러닝으로 (0) | 2021.07.14 |
| [K-DIGITAL] 미드프로젝트. 영화 별점 데이터 분석(추가) - 분류모델의 성능 향상 (0) | 2021.07.12 |
댓글 영역